Manufacturers across various industries have a clear preference for ABS Plastic when it comes to Injection Molding. This thermoplastic material is renowned for its durability, impact resistance, and versatility, making it an ideal choice for producing a wide range of products.
The benefits of using ABS Plastic in manufacturing are multifaceted. Its ability to withstand wear and tear, coupled with its resistance to impact, ensures that products made from this material have a longer lifespan. De plus, thermoplastic properties allow for easy processing and molding into complex shapes, catering to diverse product designs.
This preference for ABS Plastic is driven by its overall value proposition, combining quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Par conséquent, it remains a top choice for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality products through Injection Molding.
The Superior Properties of ABS Plastic
Le superior properties of ABS plastic make it a preferred material for injection molding due to its unique combination of characteristics. ABS plastic is known for its excellent balance of mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, which make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure
ABS plastic is a terpolymer, consisting of three distinct monomers: Acrylonitrile, Butadiene, and Styrene. The combination of these monomers provides ABS with its unique properties. Acrylonitrile contributes to the material’s chemical resistance and thermal stability, while Butadiene enhances its impact resistance and toughness. Styrene, d'autre part, provides rigidity and ease of processing.
Mechanical Strength and Impact Resistance
One of the key advantages of ABS plastic is its exceptional mechanical strength and impact resistance. The material’s toughness makes it suitable for applications where durability is crucial. ABS plastic can withstand significant stress without deforming or breaking, making it an ideal choice for consumer products and automotive components.
| Property | ABS Plastic | Other Plastics |
| Impact Resistance | Haut | Variable |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong | Variable |
| Thermal Stability | Good | Variable |
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
ABS plastic also exhibits good thermal properties and heat resistance, allowing it to maintain its structural integrity over a wide temperature range. This property is essential for applications where the material is exposed to varying temperatures. The heat resistance of ABS plastic makes it suitable for use in consumer electronics, pièces automobiles, and other applications where thermal stability is critical.
Why ABS Plastic Excels in Injection Molding Processes
When it comes to injection molding, ABS plastic stands out for its versatility and performance. The material’s characteristics make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer goods to industrial components.
Processing Ease and Flow Characteristics
One of the key advantages of ABS plastic is its ease of processing. It has a relatively low melting point and excellent flow characteristics, allowing it to fill complex molds with ease. This results in efficient production cycles and reduced energy consumption.
The material’s processing ease also contributes to its popularity among manufacturers. It can be molded into intricate shapes and designs without significant degradation of its properties, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Surface Finish Quality and Aesthetics
ABS plastic is known for its excellent surface finish quality, which is crucial for products where aesthetics play a significant role. The material can be formulated to achieve a high-gloss finish or a matte texture, depending on the desired appearance.
De plus, ABS plastic can be easily painted, printed, or coated, further enhancing its aesthetic appeal. This versatility in surface finishing makes it a preferred choice for consumer electronics, composants automobiles, and other visible parts.
Dimensional Stability and Precision
Dimensional stability is another critical factor where ABS plastic excels. It maintains its shape and size under various environmental conditions, ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications.
The precision achieved with ABS plastic injection molding is due to the material’s low shrinkage rate and its ability to retain its dimensions over time. This characteristic is particularly important in applications where tight tolerances are necessary.
Cost-Effectiveness of ABS for Manufacturing
ABS plastic is favored for its cost-effectiveness, which is crucial in competitive manufacturing environments. The economic benefits of using ABS plastic are evident in both material costs and production processes.
Material Cost Comparison
When comparing the material costs of ABS plastic with other commonly used plastics, ABS often emerges as a cost-effective option. The table below illustrates a comparison of material costs:
| Matériel | Cost per Kilogram | Relative Cost |
| ABS Plastic | $1.50 | 1.0 |
| Polypropylène (PP) | $1.20 | 0.8 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | $2.50 | 1.67 |
Production Efficiency and Cycle Times
The production efficiency of ABS plastic is another factor that contributes to its cost-effectiveness. ABS plastic has a relatively low melting point and good flow characteristics, which enable faster cycle times in injection molding processes. This efficiency reduces the overall production cost per unit.
By optimizing production processes and reducing material waste, manufacturers can further enhance the cost-effectiveness of using ABS plastic. The combination of lower material costs and efficient production processes makes ABS a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
Common Applications of ABS Injection Molded Products
ABS injection molded products have become ubiquitous in various industries due to their versatility and performance. The unique combination of properties in ABS plastic makes it an ideal material for a wide range of applications.
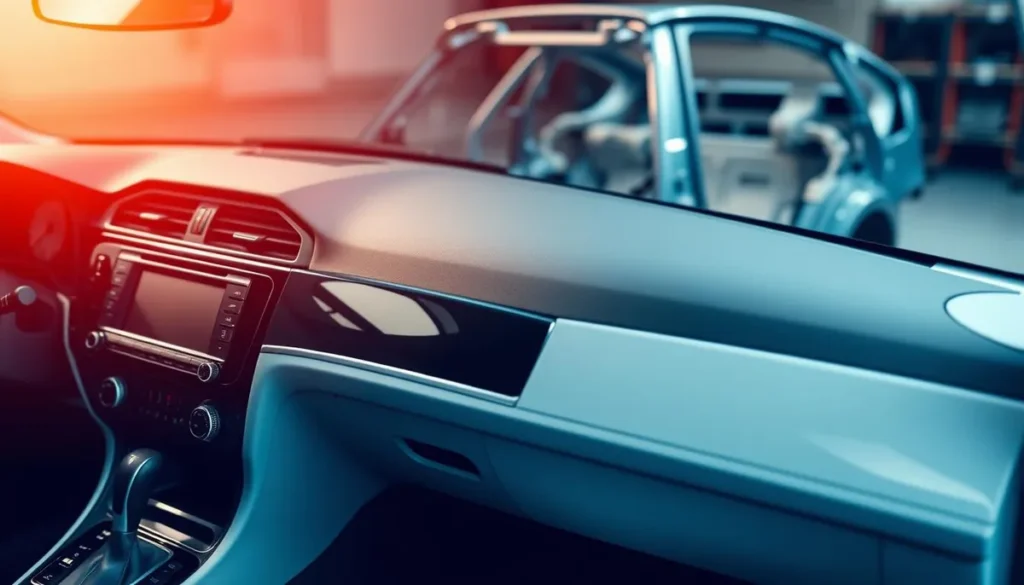
Automotive Industry Applications
The automotive industry is one of the largest consumers of ABS injection molded products. ABS is used in various automotive components, such as dashboard trim, console parts, and exterior body parts, due to its impact resistance, thermal stability, and aesthetic appeal.
- Dashboard trim and components
- Console parts and accessories
- Exterior body parts and trim
- Other interior and exterior components
Consumer Electronics and Appliances
ABS plastic is also widely used in the production of consumer electronics and appliances. Its ease of processing, surface finish quality, and dimensional stability make it a preferred material for manufacturers.
Examples of ABS injection molded products in this category include:
- TV and audio equipment housings
- Computer and laptop components
- Home appliance parts, such as vacuum cleaners and blenders
- Other electronic device casings and accessories
Medical and Healthcare Products
In the medical and healthcare sectors, ABS is used for producing various products that require high precision and reliability. The biocompatibility and sterilizability of ABS make it suitable for certain medical applications.
- Medical device housings and components
- Diagnostic equipment parts
- Other healthcare-related products
ABS Plastic vs. Alternative Materials in Injection Molding
ABS plastic is a popular choice for injection molding, but how does it stack up against other materials like polypropylene and polycarbonate? When evaluating materials for injection molding, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations.
The selection of material significantly impacts the performance, coût, and aesthetics of the final product. In this section, we will compare ABS plastic with alternative materials, including polypropylene, polycarbonate, and polyethylene, to determine their suitability for various applications.
Comparison with Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylène (PP) is a versatile thermoplastic known for its chemical resistance, elasticity, et facilité de traitement. Compared to ABS, PP has a lower density and is more resistant to chemicals. Cependant, ABS generally offers superior impact resistance and stiffness.
Key differences between ABS and PP:
- ABS has better impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability.
- PP is more resistant to chemicals, making it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments.
- ABS is generally more rigid, while PP is more flexible.
Comparison with Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a strong, transparent plastic with high impact resistance and thermal stability. Compared to ABS, PC offers superior transparency and higher heat deflection temperature. Cependant, PC is generally more expensive and may require additional processing steps.
Key differences between ABS and PC:
- PC is more transparent and has better optical clarity than ABS.
- PC has a higher heat deflection temperature, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
- ABS is generally less expensive and easier to process than PC.
Comparison with Polyethylene (PE)
Polyéthylène (PE) is a widely used thermoplastic known for its chemical resistance, flexibility, and low cost. Compared to ABS, PE has a lower density and is more flexible. Cependant, ABS offers superior impact resistance and stiffness.
Key differences between ABS and PE:
- ABS is more rigid and has better impact resistance than PE.
- PE is more flexible and has better chemical resistance than ABS.
- ABS is generally more suitable for applications requiring durability and stiffness.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
As the world shifts towards more sustainable practices, the environmental impact of materials like ABS plastic is under scrutiny. The production, use, and disposal of ABS plastic have significant environmental implications that manufacturers and consumers must consider.
The recyclability of ABS products is a crucial aspect of reducing their environmental footprint. ABS plastic is recyclable, but the process is not as straightforward as recycling other materials. The complexity of ABS recycling lies in its composition and the need for proper sorting and processing facilities.
Recyclability of ABS Products
Recycling ABS plastic involves several steps, including collection, sorting, and processing. The recyclability of ABS products can significantly reduce waste and conserve resources. Some key benefits of recycling ABS include:
- Reduction in landfill waste
- Conservation of raw materials
- Energy savings compared to producing new ABS
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Manufacturers using ABS plastic must comply with various regulatory requirements and safety standards. These regulations vary by country and region but generally aim to ensure the safe production, use, and disposal of ABS products. Key aspects include:
- Adherence to chemical safety regulations
- Compliance with product safety standards
- Proper labeling and documentation for recycling and disposal
By focusing on recyclability and regulatory compliance, manufacturers can reduce the environmental impact of ABS plastic and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
ABS plastic has emerged as a preferred material for injection molding due to its superior properties, rentabilité, and diverse applications. Its mechanical strength, impact resistance, and thermal properties make it an ideal choice for various industries, y compris l'automobile, électronique grand public, and healthcare.
The use of ABS plastic in injection molding offers numerous benefits, including ease of processing, dimensional stability, and a high-quality surface finish. As manufacturers continue to seek efficient and sustainable production methods, the recyclability of ABS products and compliance with regulatory standards become increasingly important.
In modern manufacturing, ABS plastic plays a vital role in producing a wide range of products, from automotive components to medical devices. Its versatility, combined with the advantages of injection molding, makes ABS plastic a crucial material in the production of high-quality, durable products.



https://shorturl.fm/OTCvd
ynfuj4
9kyi2a
Heya i am for the primary time here. I came across this board and I to find It really helpful & it helped me out much. I’m hoping to provide something again and aid others like you aided me.
Hi, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog site in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, great blog!
Outstanding post, I conceive blog owners should learn a lot from this site its very user friendly.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you actually realize what you are talking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally visit my site =). We could have a link alternate contract between us!
I’m still learning from you, as I’m trying to achieve my goals. I certainly love reading all that is written on your site.Keep the aarticles coming. I liked it!
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Great write-up, I am regular visitor of one?¦s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Some truly fantastic articles on this site, appreciate it for contribution.
Very efficiently written information. It will be supportive to everyone who employess it, as well as myself. Keep up the good work – for sure i will check out more posts.
I’m still learning from you, but I’m trying to achieve my goals. I certainly liked reading everything that is posted on your blog.Keep the aarticles coming. I enjoyed it!
You made some good points there. I did a search on the issue and found most people will go along with with your site.
Hello, i feel that i noticed you visited my web site so i got here to “return the prefer”.I am trying to in finding issues to improve my web site!I suppose its adequate to use some of your ideas!!
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your website, how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
Along with the whole thing that seems to be building inside this specific subject material, many of your opinions are generally fairly refreshing. Cependant, I am sorry, but I can not subscribe to your entire suggestion, all be it exhilarating none the less. It would seem to me that your comments are not entirely rationalized and in actuality you are your self not even entirely confident of your argument. In any event I did appreciate looking at it.
Very good written story. It will be helpful to anyone who usess it, including myself. Keep doing what you are doing – for sure i will check out more posts.
I dugg some of you post as I cerebrated they were handy invaluable
Great awesome things here. I?¦m very satisfied to look your post. Thanks a lot and i’m taking a look ahead to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
I haven?¦t checked in here for a while since I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I will add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
This actually answered my drawback, thanks!
You actually make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complicated and extremely broad for me. I’m looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
Great tremendous issues here. I?¦m very satisfied to peer your article. Thanks so much and i am looking ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Appreciating the hard work you put into your website and detailed information you provide. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed material. Great read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
I like reading through and I conceive this website got some genuinely useful stuff on it! .
Simply desire to say your article is as astounding. The clearness for your put up is simply nice and that i can suppose you’re knowledgeable in this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your feed to stay updated with drawing close post. Thanks one million and please keep up the enjoyable work.
F*ckin’ awesome things here. I’m very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i’m looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
I am glad to be a visitant of this stark blog! , thanks for this rare info ! .
Exactly what I was searching for, appreciate it for posting.
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks , I’ll try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Great beat ! I wish to apprentice whilst you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a weblog web site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast provided vivid transparent idea
I will immediately seize your rss feed as I can’t to find your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me recognize so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this excellent blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to fresh updates and will share this website with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
It?¦s really a great and useful piece of info. I am satisfied that you shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Awsome website! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am taking your feeds also.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
Very well written story. It will be supportive to anybody who utilizes it, as well as me. Keep doing what you are doing – can’r wait to read more posts.
I believe other website proprietors should take this web site as an example , very clean and good user friendly style.
Great – I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task.
Greetings! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could get a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having problems finding one? Thanks a lot!
A powerful share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a little analysis on this. And he the truth is purchased me breakfast as a result of I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the deal with! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I feel strongly about it and love studying more on this topic. If potential, as you develop into expertise, would you thoughts updating your weblog with more details? It’s extremely useful for me. Huge thumb up for this weblog put up!
I always was concerned in this topic and stock still am, appreciate it for posting.
益群网:终身分红,逆向推荐,不拉下线,也有钱赚!尖端资源,价值百万,一网打尽,瞬间拥有!多重收益,五五倍增,八级提成,后劲无穷!网址:1199.pw
I’ve been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this website. Reading this information So i’m happy to convey that I have a very good uncanny feeling I discovered exactly what I needed. I most certainly will make sure to do not forget this web site and give it a look on a constant basis.
Hi my loved one! I wish to say that this article is amazing, great written and include approximately all important infos. I?¦d like to see more posts like this .
Nice post. I study one thing tougher on different blogs everyday. It would all the time be stimulating to read content from other writers and observe just a little something from their store. I’d want to make use of some with the content on my blog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll provide you with a hyperlink on your internet blog. Thanks for sharing.
I went over this internet site and I think you have a lot of great info, saved to bookmarks (:.
Lovely just what I was looking for.Thanks to the author for taking his time on this one.
You have noted very interesting details! ps decent website.
Hello. impressive job. I did not anticipate this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
I gotta favorite this web site it seems very beneficial extremely helpful
I am extremely impressed along with your writing talents and also with the structure in your blog. Is that this a paid topic or did you modify it yourself? Anyway keep up the nice high quality writing, it’s uncommon to look a great weblog like this one these days..
Just a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw great layout. “Reading well is one of the great pleasures that solitude can afford you.” by Harold Bloom.
Thank you for any other informative web site. The place else may just I am getting that kind of information written in such an ideal method? I’ve a challenge that I am simply now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such info.
As I website possessor I believe the content material here is rattling wonderful , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Good Luck.
I visited a lot of website but I conceive this one has got something special in it in it
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was entirely right. This post truly made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
whoah this blog is excellent i love reading your articles. Keep up the great work! You know, many people are searching around for this information, you can help them greatly.
Hmm it looks like your blog ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to everything. Do you have any recommendations for novice blog writers? I’d really appreciate it.
Hello, Neat post. There is a problem with your website in web explorer, might check this… IE nonetheless is the marketplace leader and a good section of other folks will leave out your excellent writing because of this problem.
Downloaded the td777apk and it runs smooth. Games are decent, and the interface is clean. Not the worst way to spend an evening. td777apk
Perfect work you have done, this website is really cool with fantastic info .
I actually wanted to make a small note in order to say thanks to you for all the great advice you are giving at this site. My considerable internet research has at the end of the day been honored with awesome details to talk about with my two friends. I ‘d believe that most of us visitors actually are undeniably endowed to exist in a good site with so many perfect individuals with very beneficial pointers. I feel truly privileged to have seen your entire web page and look forward to some more awesome times reading here. Thank you again for all the details.
You have brought up a very excellent details, regards for the post.
I went over this web site and I think you have a lot of good information, bookmarked (:.
I have been exploring for a bit for any high-quality articles or weblog posts on this sort of house . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this web site. Studying this information So i’m glad to exhibit that I’ve a very excellent uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I most without a doubt will make certain to do not omit this web site and provides it a look on a continuing basis.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself? Plz reply back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know wheere u got this from. thanks
This web site is my aspiration, really superb style and design and perfect subject matter.
I’m not sure why but this blog is loading very slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
Once I initially commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a remark is added I get 4 emails with the identical comment. Is there any manner you may take away me from that service? Thanks!
Whats up very nice site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds also…I’m happy to seek out so many helpful info right here in the publish, we’d like develop more strategies on this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
Hey! Would you mind if I share your blog with my facebook group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Cheers
G’day, guys! Been having a bit of a go on goldenhoyeah1. Not bad, I must say. Graphics are alright and the gameplay’s smooth enough. Worth a look-in: goldenhoyeah1
Hey very nice website!! Man .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally…I’m satisfied to find so many helpful information right here in the put up, we want develop more strategies on this regard, thanks for sharing.
obviously like your web site however you need to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality nevertheless I will surely come again again.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
Respect to website author, some superb selective information.
Good – I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related information ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task..
You should take part in a contest for top-of-the-line blogs on the web. I’ll recommend this website!
Terrific paintings! That is the type of information that are supposed to be shared around the web. Shame on Google for no longer positioning this publish higher! Come on over and consult with my web site . Thank you =)
Hello! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing months of hard work due to no backup. Do you have any solutions to prevent hackers?
Great work! This is the type of information that are meant to be shared around the web. Disgrace on Google for not positioning this submit higher! Come on over and consult with my site . Thank you =)
I like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website :).
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your weblog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you make this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz reply as I’m looking to design my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. thanks
As a Newbie, I am always searching online for articles that can aid me. Thank you
An impressive share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing slightly analysis on this. And he the truth is bought me breakfast as a result of I found it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the deal with! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I really feel strongly about it and love reading extra on this topic. If possible, as you become experience, would you thoughts updating your blog with extra details? It’s highly useful for me. Big thumb up for this weblog post!
Thanks for the post, how can I make is so that I get an email sent to me whenever you write a fresh post?
I real happy to find this web site on bing, just what I was looking for : D as well saved to bookmarks.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more from this post. I’m very glad to see such wonderful information being shared freely out there.
Glad to be one of several visitants on this awe inspiring website : D.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. En plus, thanks for permitting me to comment!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IHJUI7TF
If you’re into the old-school stuff, classicslots777 is worth checking out. Reminds me of the good ol’ days! Might not blow your mind, but it’s a decent place to kill some time.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. Mais, I have a question, can you help me?
I will right away clutch your rss feed as I can not to find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please permit me recognise so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
These are really great ideas in regarding blogging. You have touched some good points here. Any way keep up wrinting.
I visited many web sites except the audio feature for audio songs existing at this website is actually marvelous.
These are genuinely wonderful ideas in concerning blogging. You have touched some pleasant things here. Any way keep up wrinting.
смотря смотреть онлайн 2 сезон смотреть онлайн
Need an AI generator? undress-ai.app The best nude generator with precision and control. Enter a description and get results. Create nude images in just a few clicks.
Mango777casino, my new go-to spot! The slots are fire, and the payouts are quick. Loving the bonuses too. Definitely worth a spin, broski! mango777casino
go789ac is pretty cool. I like the layout of the site. The features are user friendly. I am having a great time. go789ac
Trying my luck at 777dichoso today! The name sounds promising, so hopefully the games are too. Let’s get this bread! 777dichoso
Hey, you used to write fantastic, but the last several posts have been kinda boring… I miss your great writings. Past several posts are just a little out of track! come on!
I used to be suggested this website by my cousin. I am no longer positive whether this submit is written through him as nobody else recognize such unique about my trouble. You are amazing! Thanks!
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
I like this website very much so much fantastic info .
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
Yesterday, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Some genuinely great information, Gladiolus I found this. “What you do speaks so loudly that I cannot hear what you say.” by Ralph Waldo Emerson.
Great write-up, I am regular visitor of one¦s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Looking for Nesine? You’ve come to the right place! All your betting needs in one convenient spot. Find it all here! nesi
Bet89? Another betting site to check out! Always on the lookout for good odds and promotions. Worth my time? I’m going to bet89 to take a peak.
Looking to sign up for Plot 777 casino? The login and registration process is pretty easy. Check plot 777 casino login register on plot777loginregister.com. Good luck!
Rattling clean site, thanks for this post.
Hey There. I found your weblog the usage of msn. This is a really well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and return to learn extra of your helpful information. Thanks for the post. I will certainly comeback.